The demand for high resolution industrial cameras is driven by the markets that rely on them. Examples are healthcare, machine vision, and global security. The manufacturing of a high-performance industrial camera is a complex process that requires a lot more than the use of fasteners, connectors, and adhesives to integrate all electrical and mechanical components. The continuous miniaturization of components drives the demand for tighter tolerances, thus creating new production challenges for industrial camera manufacturers. Specific operations and measures must be taken through each stage of the process to ensure maximum performance and reliability. Proper tooling is required to guarantee the accuracy and repeatability of all steps for minimum deviations between assemblies while maintaining cleanliness from start to finish.
The stage at which the sensor is installed into the camera body is crucial to the overall performance of the camera. Sensors that are precisely and accurately attached in all critical dimensions produce clearer and crisper images. In order to provide the best seating possible, Adimec, a leader in high performance industrial cameras and imaging solutions, has developed an evolving sensor positioning system to actively align image sensors.
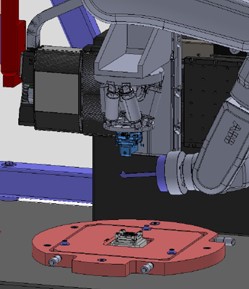
Fully automatic, 6 degree of freedom sensor alignment and fixation system work cell, with industrial articulated arm robot, long travel XZ linear translation stages and 6-DOF miniature hexapod positioning system. (Images: Adimec)
What is Active Alignment in Optics and Camera Manufacturing?
Active alignment is the type of sensor alignment that uses the real-time images to assist in the positioning of the sensor. The X and Y position, degrees of rotation, tilt, and back focal distance are all measured via feedback from the sensor as it is being aligned.
Compared to the previous passive alignment method that was good enough for more relaxed tolerances, now the tighter tolerances must be maintained on assembly machines as well as camera components, which adds complexity.
Since the image quality testing usually takes place after the camera is manufactured, faulty cameras need to be disassembled in order to be repaired or realigned. Discovering cameras are not performing to spec post-production will require time for swapping camera components and adjustments or fixes on the production machines.
The latest iteration of the Adimec system, called SPS3000, offers a manual load, fully automatic, 6 degree of freedom sensor alignment and fixation system. The modular design allows for alignment and UV-cured glue fixation of sensors sized 1/3’’ to 35mm and pixels as small as 2.5 microns. Using real-time translation of the focal plane pivot point onto the focus plane of the lens allows for perfect positioning of the focal plane.
These improvements to the alignment and positioning system allow to increase production volumes, maintain product consistency, and relocate production facilities if desired.
Active sensor alignment is one of the many values Adimec offers in their line of high-performance machine vision cameras. For more information on Adimec and its high performance industrial cameras click here.